Balancing AI's Energy Demand with Sustainability
AI's rapid growth could consume 12% of global electricity by 2030s, highlighting the need for sustainable energy solutions and efficiency innovations.
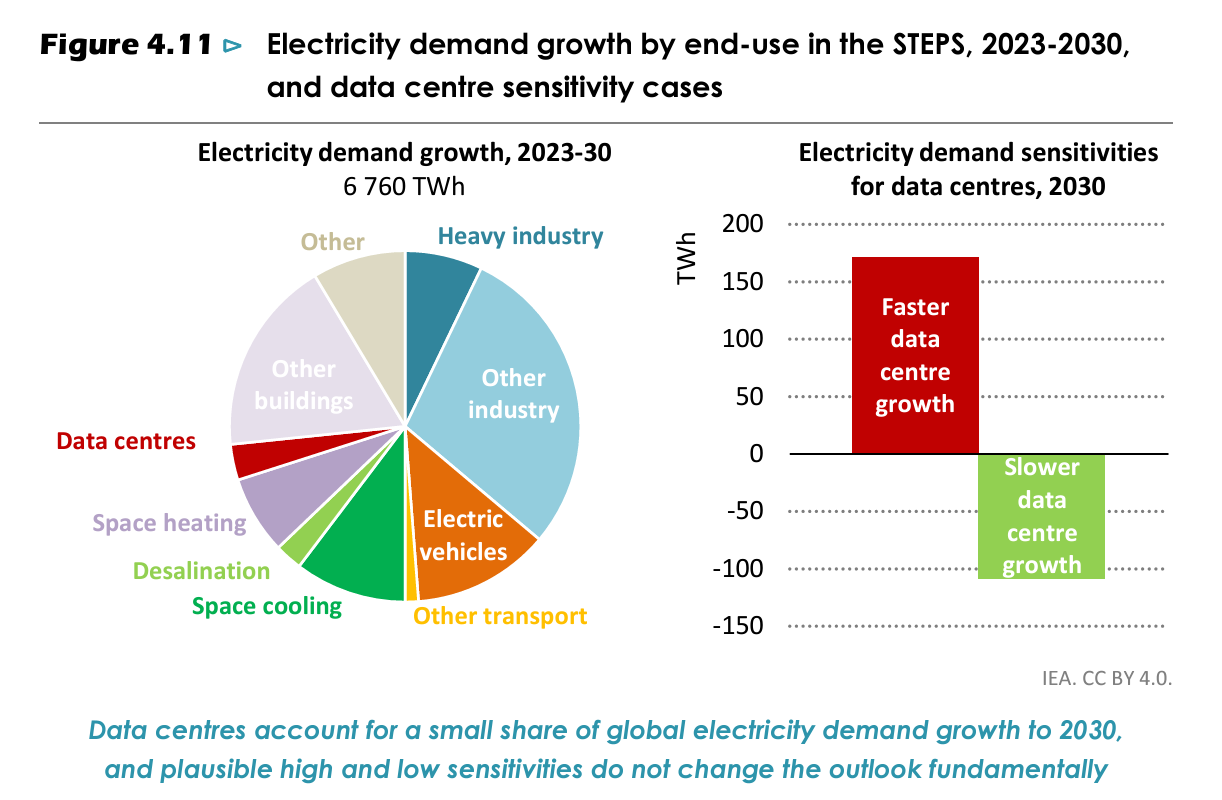
AI's Growing Demand for Electricity: Challenges and Opportunities
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has been transforming industries across the globe, from healthcare and finance to transportation and education. However, this technological boom comes with significant energy demands. Recent projections suggest that AI could consume up to 12% of the world's electricity by the mid-2030s. This staggering figure highlights both the immense potential of AI and the pressing need for sustainable energy solutions.
The Rise of AI and Its Energy Consumption
AI systems, particularly those involving machine learning and deep learning, require substantial computational power. This power is often provided by large data centers, which are energy-intensive facilities housing thousands of servers. These servers process vast amounts of data, perform complex calculations, and store massive datasets, all of which require significant amounts of electricity.
Key Drivers of AI's Energy Consumption:
-
Computational Power: AI models, especially those used in applications like natural language processing and image recognition, require extensive computational resources. This need for processing power is a major contributor to AI's energy footprint.
-
Data Centers: The infrastructure supporting AI, such as data centers, consumes a lot of energy for cooling systems, power supply, and networking equipment. As AI usage grows, so does the demand for these facilities.
-
Training and Deployment: Training AI models involves running algorithms on large datasets repeatedly, which is energy-intensive. Additionally, deploying AI models in real-world applications requires continuous updates and maintenance, further increasing energy consumption.
Challenges and Caveats
While the projection of AI consuming 12% of global electricity is alarming, there are several caveats and ongoing efforts to mitigate these impacts:
-
Efficiency Improvements: Technological advancements in chip design, like the development of more efficient processors (e.g., GPUs and TPUs), are helping reduce the energy consumption per computation. Companies like NVIDIA and Google are at the forefront of this innovation.
-
Renewable Energy Adoption: Many data centers are shifting towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce their carbon footprint. This trend is expected to continue as companies prioritize sustainability.
-
Energy Efficiency Standards: Governments and organizations are setting stricter energy efficiency standards for data centers, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices.
-
AI for Sustainability: Ironically, AI itself can be a powerful tool in managing energy consumption and promoting sustainability. AI can optimize energy usage in buildings, predict energy demand, and improve the efficiency of renewable energy systems.
Key Players and Innovations
Several key players are driving innovation in AI energy efficiency:
-
NVIDIA: Known for its powerful GPUs used in AI computing, NVIDIA has been investing in technologies that reduce power consumption while maintaining performance.
-
Google: Google's Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) are highly efficient chips designed specifically for AI workloads, reducing the energy needed for complex computations.
-
Microsoft: Microsoft is focusing on sustainable data centers, using renewable energy and innovative cooling systems to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
The prediction that AI could consume 12% of global electricity highlights the dual nature of AI's impact on society. While AI offers unparalleled opportunities for innovation and efficiency, it also poses significant environmental challenges. However, with ongoing advancements in technology and a growing focus on sustainability, there is potential for AI to not only transform industries but also contribute to a more environmentally conscious future.
As the world continues to navigate the complexities of AI's energy footprint, it is crucial for companies, governments, and individuals to work together to ensure that the benefits of AI are realized while minimizing its environmental impact. This includes investing in renewable energy, developing more efficient technologies, and using AI itself to optimize energy usage.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about AI's energy consumption and sustainability efforts:
- NVIDIA's Sustainability Report: Provides insights into NVIDIA's approach to reducing environmental impact.
- Google's Sustainability Initiatives: Offers detailed information on Google's efforts to use renewable energy in its operations.
- Microsoft's Sustainable Data Centers: Explains Microsoft's strategies for reducing the environmental footprint of its data centers.
These resources offer a glimpse into the ongoing efforts to balance the growth of AI with environmental responsibility.



