Corporate AI Adoption Triggers Wave of Workforce Reductions as CEOs Target 30% Cuts
Major corporations are accelerating AI implementation to drive significant workforce reductions, with executives targeting cuts of up to 30% as they prioritize automation over human labor. The trend signals a fundamental shift in how enterprises approach operational efficiency.
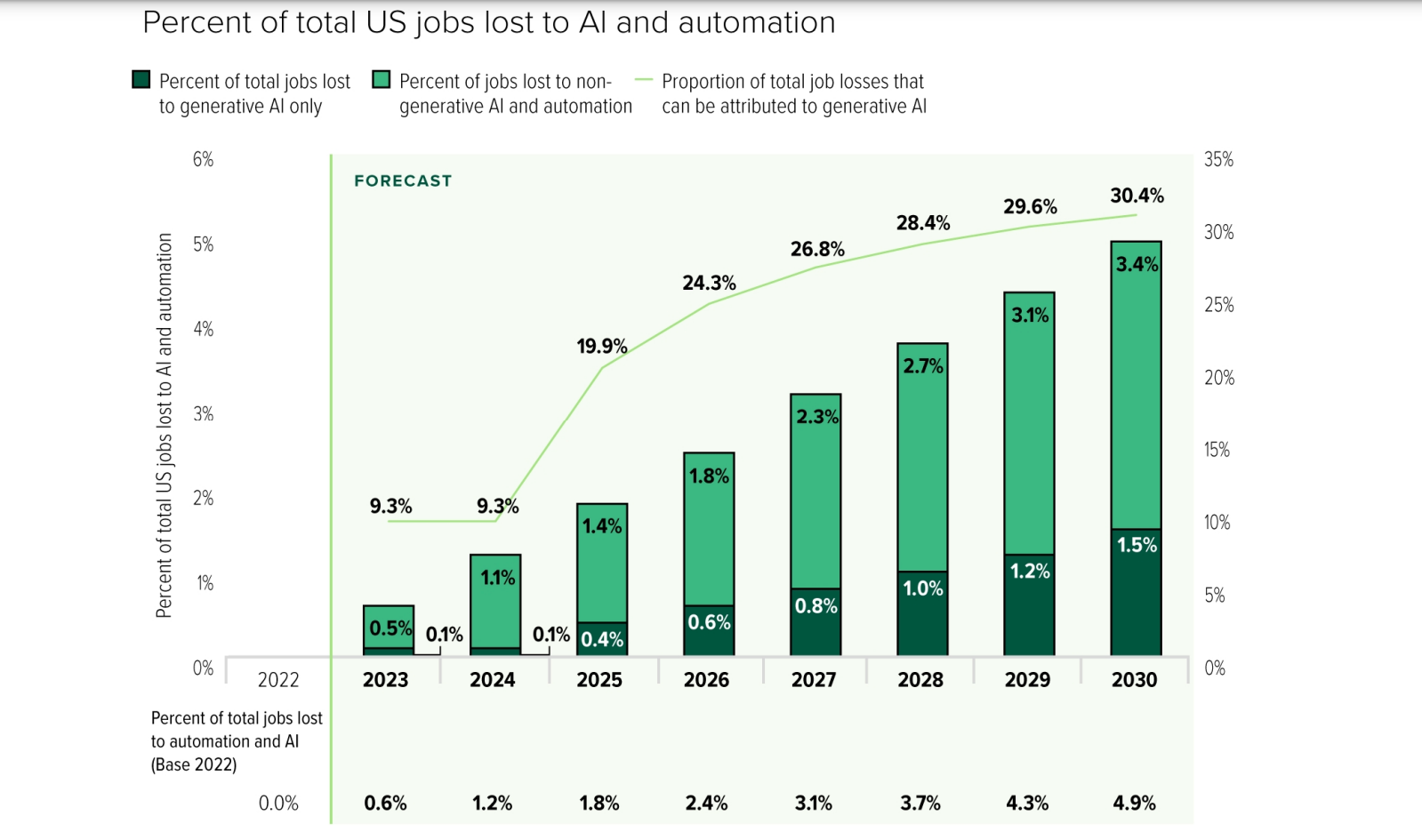
The Acceleration of AI-Driven Job Cuts
Corporate leaders are moving aggressively to deploy artificial intelligence systems across their organizations, with workforce reductions emerging as a primary objective. The scale of these cuts is substantial—many executives are targeting reductions of 25-30% of their total workforce as they implement AI-powered automation across departments ranging from customer service to software development.
This represents a marked departure from previous technology transitions. Unlike past waves of automation that unfolded gradually, the current AI adoption cycle is characterized by rapid implementation timelines and explicit cost-reduction mandates from C-suite leadership.
Why Now? The Business Case for Automation
Several factors are converging to accelerate this trend:
- Generative AI maturity: Large language models and multimodal AI systems have reached capability thresholds that make them viable replacements for knowledge work, not just routine tasks
- Competitive pressure: Companies fear falling behind rivals who adopt AI earlier, creating urgency to implement systems quickly
- Economic headwinds: Persistent inflation and investor pressure for profitability are making labor cost reduction an attractive lever
- Investor expectations: Wall Street has rewarded companies announcing significant workforce reductions, creating financial incentives for aggressive restructuring
Sectors Most Affected
The impact is not uniform across industries. Technology companies, financial services, and business process outsourcing firms are among the earliest adopters of large-scale AI workforce reductions. However, the trend is spreading to healthcare, legal services, and manufacturing as AI capabilities expand.
Customer service and back-office operations are experiencing the most immediate disruption, with AI chatbots and process automation systems replacing human workers at scale. Software development roles are also under pressure, as code-generation AI tools reduce the need for junior developers and routine coding tasks.
The Human Cost
While corporations frame these reductions as necessary adaptations to technological change, the human impact is significant. Displaced workers often lack immediate pathways to retraining, and the speed of AI adoption outpaces traditional workforce transition programs. Geographic concentration of job losses in tech hubs is creating localized labor market disruptions.
The scale of potential displacement is substantial. Industry analysts project that AI could displace millions of workers across developed economies over the next five years, with the highest-impact period occurring between 2025 and 2030.
Broader Economic Implications
The widespread adoption of AI-driven workforce reductions raises questions about macroeconomic stability. If automation proceeds faster than workers can transition to new roles, the result could be significant structural unemployment, reduced consumer spending, and widening income inequality.
Policymakers are beginning to grapple with these dynamics, though regulatory responses remain limited. Some jurisdictions are exploring AI impact assessments and worker transition support, but comprehensive policy frameworks remain underdeveloped.
What Comes Next
The trajectory appears clear: AI-driven workforce reductions will accelerate through 2025 and beyond. The question is not whether this transition will occur, but how quickly and with what safeguards for affected workers.
Organizations implementing these changes face reputational risks and potential talent retention challenges. Companies that manage transitions thoughtfully—investing in worker retraining and maintaining institutional knowledge—may gain competitive advantages over those pursuing purely extractive automation strategies.
Key Sources
- TechSpot: Analysis of generative AI's projected impact on US employment through 2030
- SQ Magazine: Comprehensive AI job loss statistics and sector-by-sector risk assessment for 2025
- TechJury: Detailed statistics on jobs displaced by automation in 2025



