Experts Warn Against Using OpenAI's ChatGPT Atlas Browser
Experts warn against using OpenAI's ChatGPT Atlas browser due to critical security vulnerabilities that could jeopardize user privacy and device security.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT Atlas Browser Faces Severe Security Warnings
OpenAI’s newly launched AI-powered web browser, ChatGPT Atlas, has come under intense scrutiny from cybersecurity experts who warn it harbors critical vulnerabilities that could put users’ data and devices at risk. Despite OpenAI's vision of revolutionizing web browsing with AI assistance, multiple independent security research firms have identified serious flaws that make Atlas—and AI browsers in general—an emerging cybersecurity threat. Experts are now urging users to reconsider the use of AI browsers until these issues are fixed.
What is ChatGPT Atlas and Why It Matters
Launched by OpenAI in October 2025, ChatGPT Atlas is a web browser integrated tightly with ChatGPT’s AI technology. It aims to redefine web interaction by allowing users to delegate tasks such as summarizing web pages, editing texts inline, and accessing agentic AI capabilities that proactively assist with browsing. OpenAI pitches Atlas as a step towards a future where web users can offload routine tasks to AI agents, streamlining digital workflows.
However, Atlas does not run code locally or install traditional extensions, but instead relies heavily on ChatGPT's AI to interpret and execute user commands embedded in natural language inputs or URLs. This architectural novelty, while innovative, has introduced a new attack surface for cybercriminals.
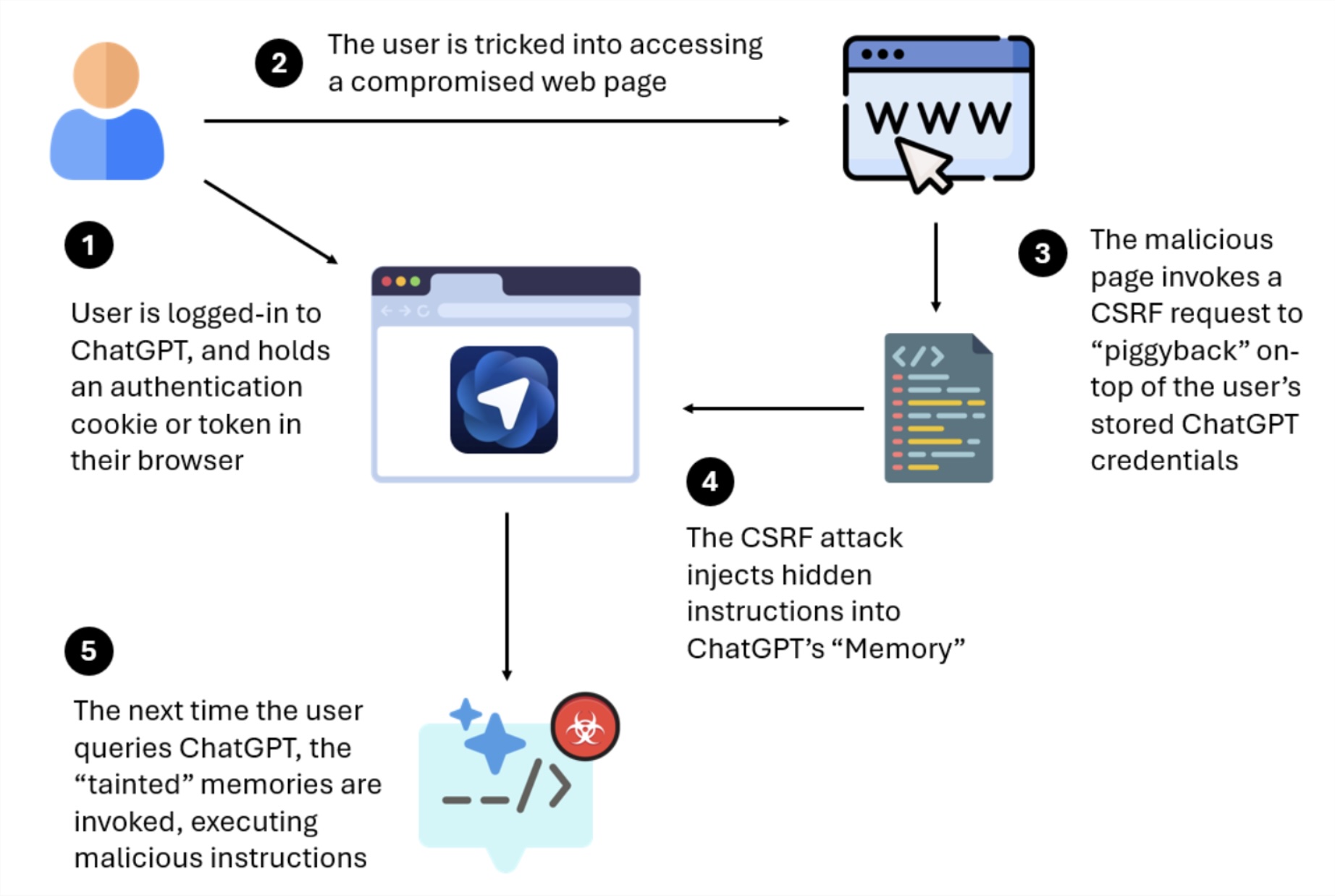
Critical Vulnerabilities Exposed
Prompt Injection and Memory Poisoning Attacks
Security researchers from LayerX Security and NeuralTrust have revealed multiple attack vectors that exploit the way Atlas processes user input and manages ChatGPT’s persistent memory.
-
Prompt Injection: Malicious actors can craft URLs disguised as benign addresses but containing hidden instructions. When Atlas processes these URLs, it interprets the embedded commands as trusted user input, enabling attackers to execute unauthorized actions or exfiltrate sensitive data.
-
Memory Poisoning via CSRF: Attackers can exploit Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerabilities to inject harmful instructions directly into ChatGPT’s memory. Once compromised, these instructions persist across browsing sessions and devices, silently hijacking the AI’s behavior to execute malicious code without detection.
Michelle Levy, head of security research at LayerX, explained, "By chaining a standard CSRF to a memory write, an attacker can invisibly plant instructions that survive across devices, sessions, and even different browsers. Subsequent normal prompts can trigger harmful actions like privilege escalation or data theft."
Lack of Anti-Phishing Protections
Testing by LayerX demonstrated that Atlas blocks only about 5.8% of phishing attempts, whereas traditional browsers like Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome block between 47% and 53%. This stark contrast means Atlas users are up to 90% more vulnerable to phishing and web-based attacks.
Real-World Risks and Examples
Beyond theoretical vulnerabilities, actual exploit demonstrations have surfaced:
-
Attackers embedding hidden “copy to clipboard” commands on malicious web pages can overwrite users' clipboards with phishing URLs, potentially stealing login credentials and multi-factor authentication codes.
-
AI browsers, including Atlas and competitors like Perplexity’s Comet, have been shown to execute hidden commands embedded in images or text summaries, exposing users to invisible attacks that traditional browsers are better equipped to block.
This class of AI browser vulnerabilities is considered more dangerous than conventional browser flaws because the AI is actively interpreting content and making decisions autonomously, massively expanding the attack surface in ways that are difficult to detect or mitigate.
OpenAI’s Response and Mitigations
OpenAI acknowledges these risks, with its Chief Information Security Officer stating the company is “very thoughtfully researching and mitigating” prompt injection and related attacks. The company has emphasized that ChatGPT Atlas cannot run code in the browser or access other apps or the file system, and that it pauses on sensitive sites to ensure user oversight.
OpenAI also encourages users to adopt a logged-out mode in Atlas to limit AI agent access to sensitive data and to monitor agent activities closely. The firm has committed to ongoing vulnerability monitoring and rapid patching as AI agents become more prevalent.
Industry and User Implications
The emergence of ChatGPT Atlas and similar AI browsers represents a paradigm shift but also introduces unprecedented security challenges. Experts warn that:
-
Until security issues are resolved, using AI browsers may expose users to greater risk than traditional browsers.
-
Developers must prioritize robust anti-phishing defenses and containment of AI agent memory to prevent persistent and stealthy attacks.
-
Users should weigh convenience against security risks, particularly when handling sensitive information or credentials via AI browsers.
Brave, the open-source browser company, has publicly highlighted the dangers of AI browsers, noting that these tools actively read and interpret web content, vastly expanding how attackers can manipulate them compared to standard browsers.
Conclusion
OpenAI’s ChatGPT Atlas browser embodies a bold future for AI-integrated web browsing but currently suffers from significant security vulnerabilities that experts warn could jeopardize user privacy and device security. Until OpenAI and the broader AI browser ecosystem implement stronger safeguards, cybersecurity professionals advise caution and recommend users avoid or limit the use of AI browsers like Atlas.
The unfolding story of AI browsers underscores the urgent need for safety-first development as AI agents become embedded in everyday digital tools. This moment is a critical inflection point in balancing innovation with security in the evolving web landscape.



