Google Launches Ironwood TPU to Challenge Nvidia's AI Chip Dominance
Google has unveiled its seventh-generation Ironwood TPU, a significant advancement in tensor processing designed to compete directly with Nvidia's market leadership in AI accelerators. The new chip represents a strategic push to establish Google as a formidable player in the rapidly expanding AI infrastructure market.
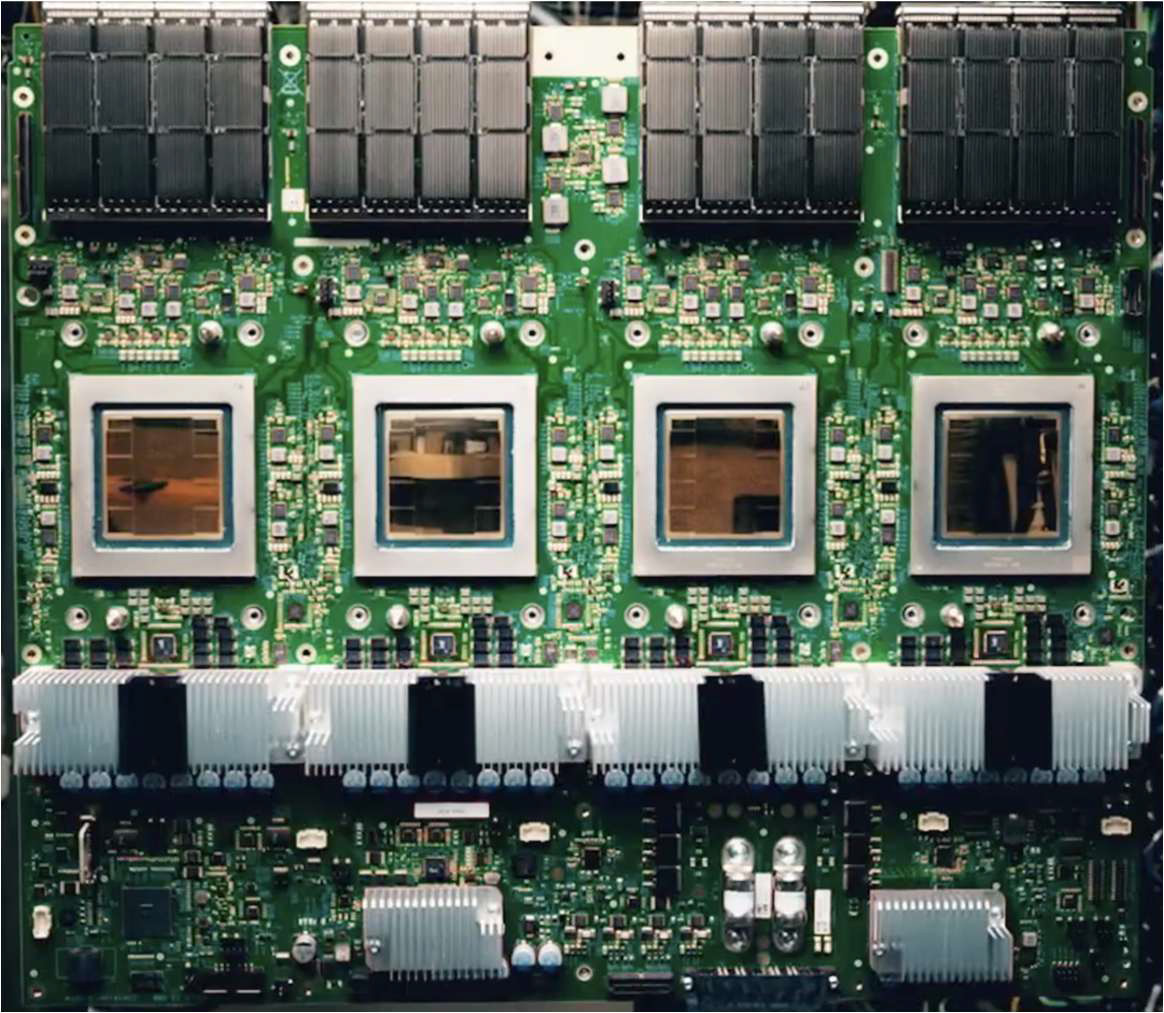
Google Launches Ironwood TPU to Challenge Nvidia's AI Chip Dominance
Google has unveiled its seventh-generation Ironwood TPU, a significant advancement in tensor processing designed to compete directly with Nvidia's market leadership in AI accelerators. The new chip represents a strategic push to establish Google as a formidable player in the rapidly expanding AI infrastructure market.
The Ironwood Architecture
The Ironwood TPU builds on Google's established tensor processing unit lineage, incorporating architectural improvements aimed at delivering superior performance for large-scale AI workloads. The seventh-generation design focuses on reasoning model capabilities, addressing a critical gap in current AI infrastructure where models require increasingly sophisticated computational resources for complex inference tasks.
Google has positioned Ironwood as purpose-built for enterprises deploying advanced language models and reasoning-intensive applications. The chip integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud's infrastructure, offering customers a vertically integrated solution that combines custom silicon with optimized software stacks.
Competitive Positioning
The launch arrives amid intensifying competition in the AI accelerator market. Nvidia currently dominates with its H100 and newer Blackwell architectures, but Google's entry with Ironwood signals the company's commitment to reducing dependency on third-party processors and offering customers alternative pathways for AI deployment.
Key competitive advantages of the Ironwood approach include:
- Custom optimization for Google's AI frameworks and workloads
- Integration with Google Cloud's broader AI services ecosystem
- Cost efficiency through vertical integration and scale
- Performance tailored specifically for reasoning and inference tasks
Market Implications
The introduction of Ironwood reflects broader industry trends where major cloud providers are developing proprietary silicon to optimize their service offerings. This strategy allows Google to:
- Differentiate its cloud platform from competitors
- Improve margins on AI infrastructure services
- Reduce reliance on external chip suppliers
- Accelerate innovation cycles for AI capabilities
Deployment and Availability
Google is making Ironwood TPUs available through Google Cloud, enabling enterprises to access the technology without significant capital expenditure. The chips are integrated into Google's infrastructure, with customers able to provision Ironwood-based instances for their AI workloads.
The deployment model emphasizes accessibility, allowing organizations of various sizes to leverage advanced tensor processing capabilities previously limited to companies with substantial hardware investments.
Technical Specifications and Performance
While specific benchmark data remains limited in initial announcements, Ironwood is designed to deliver substantial improvements in:
- Throughput for batch inference operations
- Latency for real-time AI applications
- Memory bandwidth for large model deployments
- Power efficiency compared to previous generations
The architecture supports both training and inference workloads, though the initial focus centers on inference optimization for deployed models.
Strategic Context
Google's Ironwood initiative aligns with the company's broader AI strategy, which emphasizes both consumer-facing applications and enterprise infrastructure. By controlling the silicon layer, Google can ensure its cloud platform remains competitive against Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure, both of which are pursuing similar vertical integration strategies.
The chip war in AI infrastructure is intensifying, with AMD also competing through its MI series accelerators. However, Google's advantage lies in its ability to optimize hardware specifically for its own software stack and AI frameworks.
Looking Forward
The Ironwood launch signals Google's determination to establish itself as a credible alternative to Nvidia in the AI infrastructure space. Success will depend on achieving performance parity or superiority while maintaining competitive pricing and ensuring seamless integration with enterprise workflows.
As AI workloads continue to expand across industries, the availability of multiple high-performance accelerator options benefits the broader ecosystem by preventing single-vendor lock-in and fostering continued innovation.
Key Sources
- Google Cloud Blog: Ironwood TPUs and new Axion-based VMs for AI workloads
- ServeTheHome: Google Ironwood TPU analysis and deployment architecture
- Kontronn: Comparative analysis of AI chip landscape including Ironwood, MI350, and competing architectures



