Revolutionizing AI: Cisco's Unified Supercomputing Breakthrough
Cisco's new tech unites AI data centers into a massive supercomputer, revolutionizing scalability, efficiency, and collaboration in AI infrastructure.
Revolutionizing AI: Cisco's Unified Supercomputing Breakthrough
In a groundbreaking development announced in October 2025, Cisco Systems unveiled the Silicon One P200 chip and the Cisco 8223 router, designed to connect geographically dispersed AI data centers into a single, unified supercomputing infrastructure. This innovation promises to address critical challenges in scalability, energy efficiency, and computational power as AI models grow exponentially in size and complexity.
The Challenge of Scaling AI Infrastructure
As artificial intelligence advances, the demand for computational power has surged dramatically. Training and running large language models (LLMs), generative AI, and real-time inference require massive amounts of data processing ability, often pushing the limits of traditional data center designs. Companies like Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, and Meta are investing hundreds of billions of dollars globally to expand data center infrastructure to meet these needs.
However, simply expanding physical infrastructure is increasingly unsustainable due to constraints in power consumption, cooling, and space. Top-tier GPUs used in AI workloads consume up to ten times more power than traditional servers, and the scale of modern AI training facilities can cover thousands of acres with energy demands reaching gigawatts.
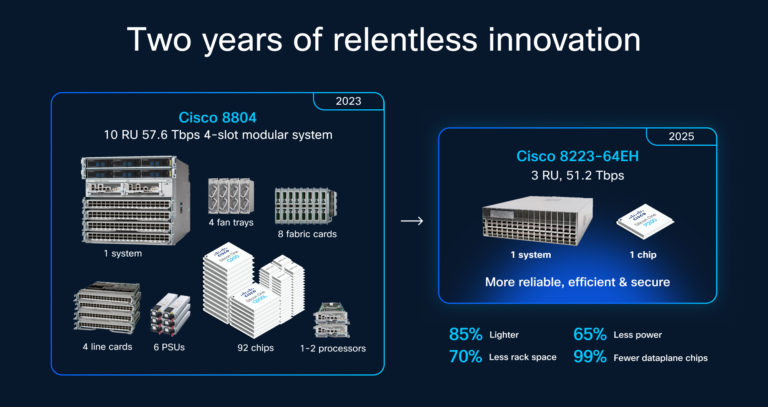
Cisco’s Breakthrough: Silicon One P200 and 8223 Router
Cisco’s new hardware aims to revolutionize how AI data centers are interconnected. The Silicon One P200 chip and accompanying 8223 router enable ultra-high-speed, long-distance connectivity between AI data centers, effectively allowing them to operate as one colossal supercomputer. This means that instead of isolated clusters processing AI workloads independently, multiple data centers dispersed geographically can share workload seamlessly, pooling their compute, storage, and networking resources.
This capability is particularly critical as AI training workloads become too large to fit within a single data center and require distribution across multiple sites — often chosen for factors like lower power costs or better regulatory environments. Cisco’s technology addresses the bottleneck in supercomputing performance, which has shifted from processing chips themselves to the networking fabric that connects them.
Industry Context: Growing AI Supercomputing Efforts
Cisco’s announcement aligns with a broader industry trend toward massive AI supercomputers and integrated compute environments:
-
MIT Lincoln Laboratory Supercomputing Center (LLSC) recently unveiled TX-Generative AI Next (TX-GAIN), the most powerful AI supercomputer at any U.S. university, featuring over 600 NVIDIA GPUs and delivering two AI exaflops of peak performance.
-
Huawei’s Atlas 900 A3 SuperPoD and upcoming Atlas 960 SuperCluster represent the company’s push to build superclusters with unprecedented scale, integrating over a million NPUs (neural processing units) and targeting zettaflops-level performance for AI workloads.
-
Nvidia emphasizes the concept of data centers as a single, enormous “intelligence manufacturing factory,” where the integration of GPUs, interconnects, and software stacks is crucial for efficient AI model training and inference.
-
Quantum computing and AI are also converging, as seen in a new Quantum-AI data center in New York, developed by OQC, Digital Realty, and Nvidia, which combines superconducting quantum computing with AI supercomputing.
Implications of Unified AI Data Centers
The ability to link multiple AI data centers into one unified supercomputer offers several critical advantages:
-
Scalability: AI workloads, especially very large models, can be distributed across multiple data centers without sacrificing speed or efficiency.
-
Energy Efficiency: By enabling workload distribution, companies can optimize power use by locating parts of the workload in regions with lower energy costs or renewable energy sources.
-
Resilience and Flexibility: Distributed supercomputing infrastructure can provide redundancy and better failover capabilities, enhancing reliability.
-
Cost Reduction: Avoids the need to build ever-larger single data centers, which become increasingly expensive to power and cool.
-
Global Collaboration: Facilitates cross-border AI research and development by allowing institutions and companies to share computational resources while managing data locality and compliance considerations.
Future Outlook: The Next Era of AI Infrastructure
Cisco’s Silicon One P200 and 8223 router mark a pivotal moment in AI infrastructure evolution. As AI models scale beyond hundreds of billions of parameters into the trillions, and as enterprises push toward real-time, large-scale AI applications, the network fabric connecting AI hardware becomes a critical bottleneck. Overcoming this bottleneck enables a new paradigm of hyper-distributed supercomputing.
This trend is expected to accelerate investments in intelligent infrastructure that goes beyond raw GPU counts to include cutting-edge networking, software integration, and energy-efficient designs. Analysts predict that data center switch sales focused on AI workloads could reach nearly $80 billion over the next five years, underscoring the commercial potential of these innovations.
Visualizing the Future
-
Cisco Silicon One P200 Chip and 8223 Router: Images of these components showcase the hardware designed to enable unprecedented long-distance AI data center connectivity.
-
AI Supercomputing Clusters: Visuals of MIT’s TX-GAIN and Huawei’s Atlas SuperClusters illustrate the scale and complexity of modern AI infrastructure.
-
Global Data Center Networks: Diagrams demonstrating how multiple data centers interlink to function as a single AI supercomputer provide insight into architecture and flow.
The move toward uniting AI data centers into one massive supercomputer reflects a fundamental shift in how AI workloads will be managed and scaled in the future. Cisco’s breakthrough technology, along with parallel advancements from industry leaders, sets the stage for AI research and deployment at an unprecedented scale and efficiency, promising to accelerate innovation across fields from natural language processing to climate modeling and beyond.



