AI to Intensify Cyberattacks by 2025, Experts Warn
AI is transforming cybercrime, with damages estimated at $10.5 trillion by 2025. Governments and industries are urged to innovate and collaborate against AI-driven threats.
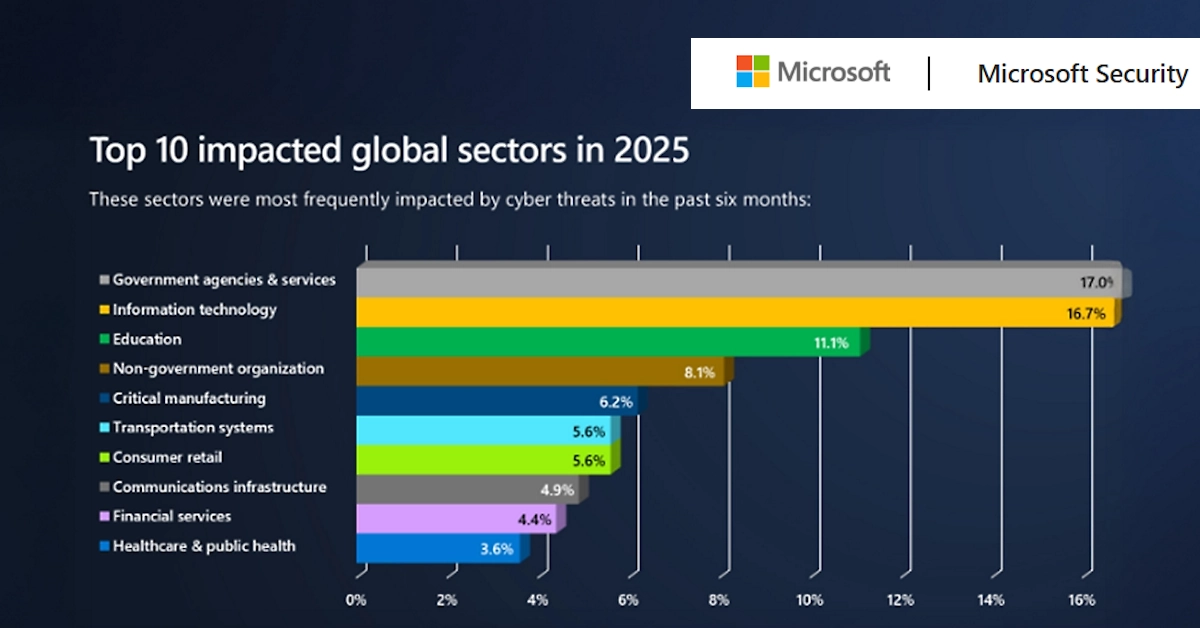
AI Is About to Supercharge Cyberattacks: A Critical Cybersecurity Turning Point in 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) is dramatically transforming the landscape of cybercrime, fueling an unprecedented surge in sophisticated cyberattacks that threaten global economic stability and individual security. In 2025, cybercrime damage is estimated at a staggering $10.5 trillion worldwide, with AI playing a central role in both enabling attackers and challenging defenders. As AI technologies become more accessible and powerful, cybercriminals are leveraging them to automate, scale, and personalize attacks, fundamentally altering the nature of digital threats.
How AI Is Amplifying Cyber Threats
Cyber adversaries use AI to enhance multiple facets of their operations:
-
Automated and Personalized Social Engineering: AI algorithms generate highly convincing phishing emails, texts, and voice messages that mimic human writing styles and speech patterns. These AI-driven social engineering attacks are now responsible for over 80% of phishing emails, representing a 53.5% increase year-over-year. Microsoft's 2025 Digital Defense Report highlights AI-powered phishing as three times more effective than traditional campaigns.
-
Deepfakes and Impersonation Fraud: Generative AI can create near-perfect synthetic voices and faces, enabling fraudsters to produce fake video calls, press statements, or identity impersonations that deceive victims and bypass security checks. This technology facilitates new attack vectors that complicate trust verification.
-
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Cybercriminal networks now offer AI-enhanced ransomware toolkits to affiliates, democratizing access to advanced attack tools. These kits automate data encryption and double extortion tactics, threatening data destruction and public data leaks simultaneously.
-
Synthetic Identities and Credential Theft: AI aids in creating synthetic identities and automating the extraction of valuable personal information, which attackers use to infiltrate systems at scale.
AI-driven attacks are faster, more scalable, and harder to detect. They enable mass exploitation with minimal human oversight, allowing attackers to simultaneously target thousands of systems while tailoring attacks to individual victims. Approximately 40% of cyberattacks now incorporate AI components, underscoring the technology's central role in modern cybercrime.
Industry and Government Responses
The rapid evolution of AI-enabled cyber threats has prompted urgent calls for new defense paradigms. According to Microsoft’s 2025 Digital Defense Report, traditional security approaches are insufficient against AI-enhanced adversaries, who operate with greater volume and precision than ever before. The report stresses the need for international collaboration to establish coordinated defenses and enforce norms against cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure and essential services.
Governments worldwide are responding with sweeping AI-related policies and regulatory frameworks. Over 70 countries are expected to implement AI policies focused on cybersecurity, ethical AI use, and risk reduction by 2025, building on previous efforts from more than 50 nations. These initiatives include:
- National AI strategies integrating cybersecurity measures.
- Specialized AI councils and inter-agency task forces.
- Legal frameworks designed to promote transparency, accountability, and safeguard against AI misuse.
Despite these efforts, business and cybersecurity leaders remain pessimistic about AI’s net impact on cyber defense. A 2025 survey by AlixPartners found only 9% of leaders believe AI gives cybersecurity teams an advantage over attackers, while 56% think cybercriminals benefit more from generative AI tools. This sentiment highlights the urgent need for organizations to develop proactive and adaptive security strategies.
The Rising Cost and Societal Impact
The financial toll of AI-enhanced cybercrime is immense and growing. Cybersecurity Ventures projects the global cost of cybercrime to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2025, with forecasts reaching $13.82 billion by 2028. These costs encompass ransomware payments, data recovery, lost productivity, reputational damage, and broader economic disruption.
Cyber threats increasingly intersect with geopolitical conflicts and criminal enterprises, extending their impact beyond technical issues to societal and economic domains. The erosion of trust in digital communications and services threatens individual safety, business continuity, and national security.
Key Recommendations for Organizations
To mitigate AI-driven cyber risks, experts recommend:
-
Adopting AI-Driven Security Tools: Leveraging AI for threat detection, response automation, and predictive analytics to keep pace with evolving attacks.
-
Enhancing Employee Awareness: Training employees to recognize sophisticated AI-crafted social engineering attempts.
-
Implementing Robust Data Governance: Restricting the use of internal and proprietary data with public AI tools to minimize leakage and misuse, a practice adopted by 73% of surveyed organizations in 2025.
-
Participating in International Cooperation: Engaging in cross-border initiatives to define cybersecurity norms and collaborative defense mechanisms.
Visual Illustrations
Relevant images to accompany this analysis include:
- Infographics showing the rise of AI-powered phishing and ransomware attacks.
- Visuals from Microsoft’s 2025 Digital Defense Report illustrating AI’s role in the threat landscape.
- Diagrams of deepfake technology and AI-driven social engineering methods.
- Logos of key cybersecurity initiatives and international AI policy forums.
The accelerating integration of AI in cyberattacks marks a pivotal moment in cybersecurity history. While AI offers powerful tools for defense, the current imbalance favors attackers equipped with generative AI capabilities. The global community must urgently innovate, regulate, and collaborate to secure the digital future against AI-supercharged threats.



